Welcome to our guide on how to set up a network for your small business. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to improve your existing setup, a reliable and efficient network is a cornerstone of modern business operations. It enables seamless communication, facilitates easy sharing of resources, and can significantly enhance your operational efficiency. If you're not entirely familiar with the technical jargon, don't worry—we've got you covered. This post will walk you through the basics of setting up a network.
How to Set Up a Network (Step By Step Guide)
→ Plan network layout
→ Install hardware (routers, switches)
→ Configure network hardware
→ Set up wireless access points
→ Configure network management software
→ Test the network
→ Maintain & update regularly
You don’t need to be a tech specialist to set up a network for your small business (although some essential IT skills can help make the process easier). Here’s our quick guide to setting up a network.
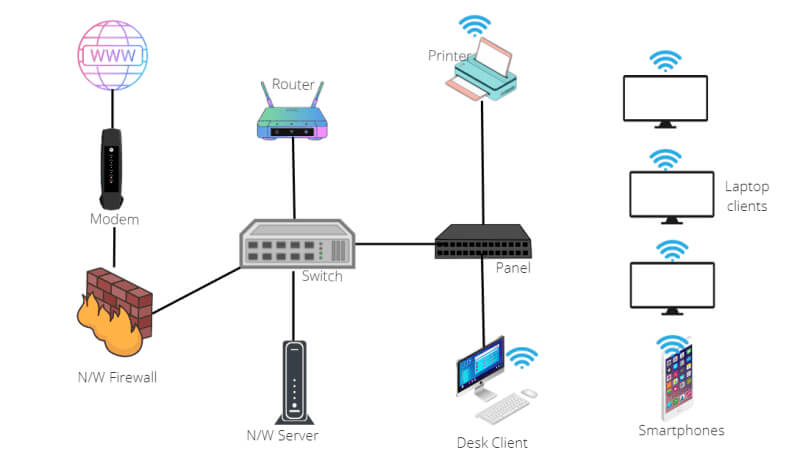
Step 1: Plan Your Network Layout
- Determine the number of devices, types of devices (computers, printers, servers, etc.), and their locations within your office.
- Sketch a layout of your office and plan where each device will go and how they will connect to the network. Decide on the locations for routers and switches, ensuring they are central and accessible.
Step 2: Install Physical Infrastructure

- For a wired network, run Ethernet cables from each device back to the switch or router. Use cable organisers to keep cables tidy and safe from damage.
- Connect your router to your modem, and then connect switches to the router if needed to expand the number of available ports.
- Plug the Ethernet cables from your devices into the switch or router. Ensure each connection is secure.
Step 3: Configure Your Network Hardware
- Your network hardware will come with instructions on how to set up your chosen hardware.
- Use a web browser to log into the router’s interface using the IP address provided in the router’s manual. This is typically something like 192.168.1.1.

- Configure basic settings such as network name (SSID), password, and encryption type for security. For businesses, WPA2-Enterprise is recommended.
Step 4: Set Up Wireless Access Points
- Place wireless access points in strategic locations to make sure there is complete coverage across your office. Avoid physical obstructions and interference sources like microwaves or cordless phone bases.
- Similar to your main router, access each point's interface to set up network names, security settings, and other configurations. Ensure each access point is on a different channel to reduce interference.
Step 5: Configure Network Management Software
- Install any network management software you have chosen, such as SolarWinds, Cisco Meraki, or others (we’ve listed some common ones below).
- Set up monitoring for traffic, usage patterns, and potential security threats. Configure alerts for any unusual activity.
- Whatever network management software you choose will have its own manual on how to do this.
Step 6: Test Your Network
- Make sure every device can connect to the network and has internet access.
- Use a network testing tool (like Ookla Speedtest) to check the speed and coverage area of your wireless network. Adjust the placement of access points if there are dead zones.

- Run a security audit to check for vulnerabilities and ensure all settings are properly configured.
Read more: How to Perform a Vulnerability Assessment
Step 7: Maintain and Update Regularly
- Keep your router, switches, and access points updated with the latest firmware to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Regularly check network performance and make adjustments as needed based on traffic patterns and growing business needs.
Setting Up a Network – Common Terms Explained
Setting up a network for the first time can be confusing if you’re not familiar with the technical jargon. Here are some basic networking terms explained:
Basic Networking Terms
- LAN (Local Area Network): This is a network that connects computers and devices in a limited area, such as an office building, school, or home. A LAN allows for fast communication and sharing of resources like files and printers within a local setting.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): Unlike a LAN, a WAN covers a broad area. This could be a network connecting several offices across cities or even countries. The internet is the largest WAN, connecting networks worldwide.
- Routers and Switches: These devices are the backbone of any network. A router directs data traffic between different networks, while a switch connects devices within the same network, allowing them to communicate.
Types of Networks
- Wired Networks: These networks use cables (like Ethernet cables) to connect devices. Wired networks are typically faster and more secure than wireless ones, making them a good choice for businesses that handle large files or sensitive information.
- Wireless Networks: These networks use Wi-Fi to connect devices without the need for physical cables. They offer more flexibility and ease of installation. However, they can be less secure and might suffer from interference issues, affecting their performance.
Planning Your Network
Setting up a network that meets your small business needs requires careful planning and foresight. Here’s how to get started:
Assessing Business Needs and Network Size
- Start by determining how many devices will need to connect to the network, including computers, printers, phones, and other smart devices.
- Think about how your business might expand in the future. Your network should not just meet your current requirements but also accommodate future growth without costly overhauls.
Importance of Scalability and Flexibility
- Ensure that the network can scale up easily—this means adding more devices or bandwidth as your business grows.
- Your network should also be flexible enough to integrate new technologies and adapt to changes in how your business operates.
Budget Considerations
- While it’s tempting to cut costs initially, consider the long-term benefits of investing in a robust network that won’t require frequent upgrades.
- Look for solutions that offer the best balance between cost, performance, and scalability.
Choosing the Right Hardware and Software
Selecting the right tools is crucial for building a network that’s secure, efficient, and capable of supporting your business operations.
Hardware Selection Guide
- Routers and Switches: Choose routers with enough capacity and security features to handle your data traffic. Switches should be selected based on the number of devices to connect and the type of network traffic you expect.
- Modems and Network Cables: Opt for modems that are compatible with your internet service provider and offer high-speed connectivity. Quality network cables are crucial for wired networks to minimise data loss and interference.
Recommendations for Network Management Software
- User-Friendly Interface: Look for software that offers a user-friendly interface and robust functionality to monitor and manage your network efficiently. Here are some examples of popular network management software in Australia:
- → SolarWinds
- → Paessler PRTG
- → ManageEngine
- → Cisco Meraki
- → Zabbix
- Features: Essential features might include network security management, performance monitoring, and remote access capabilities.
Importance of Security Features
- Routers and Firewalls: Ensure your routers have built-in security features like firewall protections, VPN capabilities, and guest network functionalities. These help protect sensitive data and ward off potential cyber threats.
- Regular Updates: Regular software updates are crucial to protect your network from new vulnerabilities and ensure it runs smoothly.
Take Your IT Skills to New Heights with Online Courses Australia
Ready to take your IT skills to the next level? Enrol in our online Essential IT Skills Course. Whether you're a small business owner, a budding entrepreneur, or simply looking to boost your professional toolkit, our online Essential IT Skills Course is designed for you.
IT skills aren't just for tech professionals—everyone can benefit from understanding the basics of networking, cybersecurity, and system management.
Don't miss out on this opportunity to enhance your career with essential IT skills that are in high demand.
DOWNLOAD ESSENTIAL IT SKILLS COURSE INFO PACK
How to Set Up a Network FAQs
What type of network should a small business use?
For a small business, the ideal network type often depends on your specific needs and budget. A hybrid network that combines both wired and wireless elements tends to be quite effective. Wired connections can ensure stability and speed for critical devices, while wireless access accommodates mobile devices and provides greater flexibility around the workplace.
How much does it cost to set up a network for a small business?
Setting up a network for a small business can vary significantly in cost, typically ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars (AUD). For most small setups involving a router, a few access points, and basic infrastructure, you might expect to start around $500, but costs can rise with more complex needs and higher-quality equipment.
How do I set up a small office network?
To set up a small office network, you’ll first want to assess your needs to determine how many and what types of devices you’ll be connecting to. Install a reliable modem and router, and configure your router with secure settings, including a unique SSID and strong password. Finally, connect all devices to the network and make sure they have stable internet access.
How do I set up a small business Wi-Fi network?
Setting up a Wi-Fi network in a small business involves choosing a router that can handle your expected traffic volume and provides robust security features. Place the router in a central location to optimise coverage across the office. Be sure to secure the network with strong encryption and a secure password to protect your business data and maintain network integrity.
Read more:
- Career Development





















